Structural safety cannot be based on perception — it requires precise data to manage risks. STRUCTURAL & GEOTECHNICAL MONITORING is the scientific solution for tracking, evaluating, and detecting early signs of instability in a structure, both during construction and throughout its operational life. From controlling settlement and tilt to providing warnings for cracks or abnormal deformation, monitoring plays a critical role in ensuring every structure remains safe, durable, and performs as designed. If you are seeking an optimal solution to protect your structure and its occupants, the professional monitoring services from E2CS.
1. Objectives of Structural Monitoring

The main objectives of monitoring work include:
- To determine the settlement and displacement (both absolute and relative) of a structure compared to its original design.
- To assess the stability of the foundation soil and the structure itself.
- To provide real-world data that helps refine the accuracy of geotechnical parameters used in analysis.
- To validate design calculation methods and establish permissible limits for movement.
- To identify the root causes of settlement or tilt and propose preventive or remedial solutions.
- To support the project commissioning and acceptance process and to maintain technical archives.
2. Scope and Procedure of Structural Monitoring
Structural monitoring typically consists of two main components: settlement monitoring and tilt monitoring.
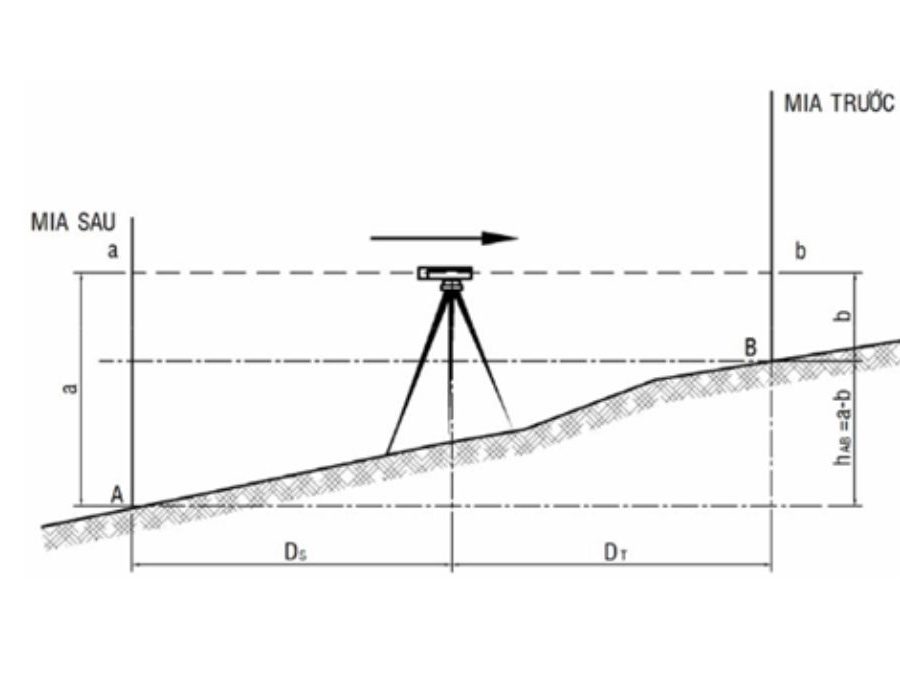
- Settlement Monitoring: The process begins with the establishment of benchmark points and monitoring stations. Based on the project’s requirements, a suitable measurement frequency is defined. Depending on site conditions and structural characteristics, measurement methods such as leveling or GPS may be employed. Collected data is then processed to evaluate the stability of the benchmarks, followed by the preparation of detailed settlement reports to support technical supervision and quality control.
- With tilt monitoring, this involves installing reference benchmarks and tilt monitoring points at strategic locations prone to deformation. After setting an appropriate monitoring schedule, measurements are taken to calculate tilt angles and assess the overall vertical alignment and stability of the structure. The goal is to detect any early signs of movement that could impact structural safety or serviceability.
3. Key Monitoring Parameters
- Vertical displacement: including settlement, deflection, and heave
- Horizontal displacement: lateral movements or shifts in structural position
- Inclination: deviation from vertical (plumbness)
- Cracks: monitoring crack width, length, and progression over time
4. When Is Structural Monitoring Required?
Structural monitoring should be conducted during both construction and operation phases. During construction,it helps track settlement and tilt caused by increasing structural loads, ensuring the structure is built safely and in accordance with the design. During operation,it becomes crucial when signs of abnormal behavior appear—such as cracks, tilting, or localized settlement—or when there are changes in loads or service conditions, allowing timely detection and mitigation of potential risks.
Structural monitoring is not only a regulatory requirement but also an effective technical solution to ensure long-term safety, stability, and performance . Proper implementation minimizes risks, protects users, and optimizes future repair and reinforcement costs. Detailed guidelines are provided in Decree No. 06/2021/ND-CP on the Management of Quality, Construction Execution, and Maintenance of Construction Works..


